If you are considering deploying an RFID solution, you will want to have a better understanding of how RFID technology works.
To help you learn more, I’ll be covering the key aspects of RFID tags and their various types to better help you break down which one you want to use in your environment.
I’ll also be giving real-world application examples to help you understand how you can implement your own RFID solutions.
RFID technology can help streamline many business processes and for this reason, it is becoming more and more popular.
What are RFID Tags?

RFID stands for “Short Frequency Identification” and these smart barcodes are attached to items in order to easily identify them by using radio frequency technology.
In more simple terms, radio waves transmit data from the tag to the reader that then transmits the information to a RFID computer program.
A common example of RFID tags being used is at the grocery store.
Smart barcodes are placed on products in order to easily identify them at checkout.
When you go to checkout, the smart barcodes are scanned to bring up the product information and price.
On the back-end, the barcode information is entered into the computer system and helps the store manager keep track of inventory, demand, items sold, etc.
This information is not only useful in creating a quick and streamlined checkout process for customers, but it creates useful information for store managers to track which items need to be re-stocked and they can look at product trends and determine items that are more or less profitable.
Frequently, RFID tags are what people use for merchandise tracking and theft prevention.

You can have unique details like the EPC or GS1 Electronic Product Code™, individually programmed into every RFID tag that can get affixed to pallets, boxes, products, as well as equipment of high value.
If you want to get the easiest explanation on RFID labels, the best way to do this to compare them with barcodes.
Similar to the barcodes, RFID tags are used to immediately get the information that you need on the level of the product or pallet.
Since radio wave technology is what RFID tags utilize, being in the direct line-of-sight may not be a requirement – giving you the ability to have products in whole truckloads or pallets read for as fast as 700 products per second.
RFID tags are clearly advantageous whenever driving efficiency and visibility become involved in the level of the supply chain.
This is referred to as smart label tracking.
Aside from the great benefits that RFID technology provides to supply chain and distribution, there have been a lot of brands that have leveraged RFID tags as it allows their customers to become engaged in a personal manner.
Clients are able to scan the RFID label with their phone and are directed to landing pages specific to a product, restaurant menu, or educational content.
RFID tags are also used on vehicles.
For example, many rental car companies use RFID tags to track their rental vehicles and automatically check the cars in or out of the lot in real time.
In the case of animals or humans, the RFID tags may also be called RFID chips.
RFID chips are used to keep track of pets and find them if they wander off and they are even used on senior citizens with Alzheimer’s disease.
These are just a few examples of how RFID technology works, but there are so many more ways that RFID technology helps streamline and simplify business processes.
Sending and receive information to and from the tag and the reader by using radio waves is what RFID technology depends on.
Radio frequency identification tags encompass near field communication (NFC) tags, ultra-high frequency (UHF) tags, and more.
How do RFID tags work?

RFID tags work by using a microchip and an antenna to receive and transmit information.
People sometimes refer to this as an IC or integrated circuit.
The RFID tags comes in two main types: these are passive and battery-operated.
Just as the name suggests, RFID tags that are battery-operated use an onboard battery as their power supply.
RFID tags that are operated with a battery may also be referred to as active RFID tags.
Whenever the RFID tag is passive, it works through the use of electromagnetic energy that gets transmitted from the RFID reader.
Passive RFID Tags
Passive RFID tags transmit information in three different frequencies:
- UHF or Ultra-High Frequency tags – 300 MHz to 3GHz
- HF or High Frequency tags – 3 to 30 MHz
- LF or Low Frequency tags – 30 KHz to 300 KHz
The frequency used can affect the range of the tag.
Whenever the reader scans the passive RFID tag, the energy is transmitted by the reader to the tag.
With this, the antenna and the chip get enough power so that the information can be relayed back to the reader and the reader will have the information transmitted back to the RFID computer program so it can get interpreted.
There are two main types of passive RFID:
- Hard tags
- Inlays
Hard tags are similar to what its name suggests – they are made out of hard and durable materials like metal or plastic.
Inlays are usually quite thin and can come in the form of stickers that you can place on products or on different materials.
Active RFID Tags
Active RFID tags use one of two frequencies to transmit information which is either 915 MHz or 433 MHz.
These come in three main parts that include the interrogator, antenna, and tag.
The active RFID tag must have a battery that can sufficiently supply power for three to five years.
In case it dies, you need to have the unit replaced as the batteries are irreplaceable.
The active RFID tags come in two main types: these are transponders and beacons.
Transponders are similar to the passive RFID tags wherein using the reader is required to transmit data.
An information ping in every few seconds is what beacons send out.
They have a signal that is readable from hundreds of feet away.
Since they frequently send out information, they have a battery that has the tendency to quickly deplete.
Similar to the passive RFID tags, transponders need to use a reader whenever they want to transmit information.
Within one another’s range, the reader will initially have a signal sent to the transponder and eventually ping the relevant information back.
Since they only get activated whenever they are near a reader, the transponders can be more efficient in using the battery compared to the beacons.
A Comparison of the Different Types of RFID Tags: LF RFID, HF, UHF, and NFC
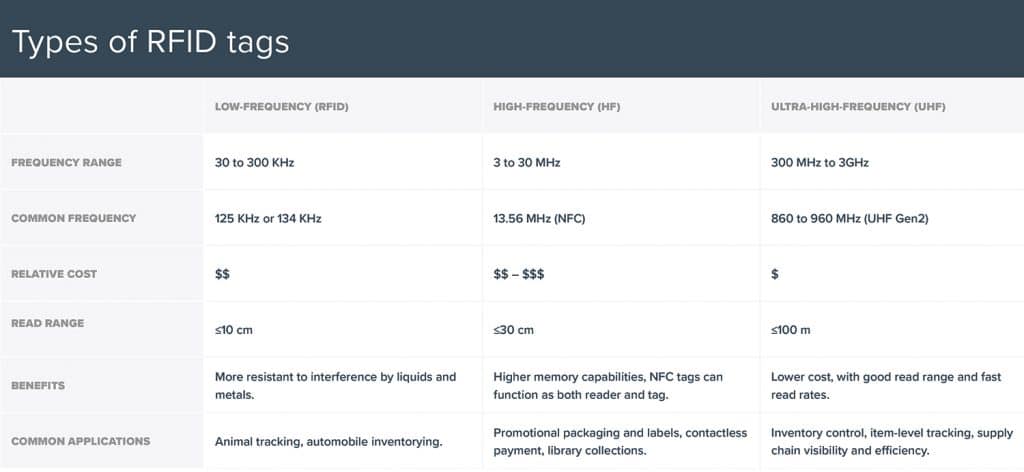
There are many RFID tags available in today’s market and they differentiate according to the range of frequency which can be low, high and ultra-high.
As mentioned above, RFID tags are either battery-assisted or semi-passive, passive or un-powered, and active or powered.
RFID Tags with Low-frequency From 30 kHz to 300 kHz
Whenever the RFID tags have a low frequency, their read ranges are shorter and lead rates are slower compared to the HF or UHF.
However, since they come at a longer wavelength, they can be less susceptible to interference from metals and liquids.
Since that is the case, people often use them in applications wherein the RFID labels get affixed to a substrate made of metal.
This includes keeping the inventory for automobiles and beer kegs.
RFID Tags with UHF or ultra-high-frequency from 300 MHz to 3GHz
People consider UHF RFID tags as the “supply chain frequency” as they can generally have a lower price compared to the other types.
Aside from that, they can also provide great rates and read ranges.
They are commonly applied to driving efficiencies in the supply chain, controlling the retail inventory, and tracking at the level of an item.
The DoD (Department of Defense) and brands like Target and Wal-Mart have mandated their suppliers to have every pallet and product labeled with RFID tags.
Having these labels can lessen the need for doing manual inventories because it simultaneously reads hundreds of tags.
It can also allow people to become more accurate in identifying the incoming inventory as it reads products in entire truckloads every time.
RFID Tags with HF or High-Frequency from 3 to 30 MHz
Since HF RFID tags have greater memory capabilities and a longer read range, they can be well-suited when it comes to creating a catalog of library media.
They are also great to use as tracking bracelets for kids or pets.
In this RFID HF category, it comes with the common kind of smart label that are NFC or Near Field Communication Tags.
A Comparison Between HF RFID and NFC
The NFC tags are under a subcategory of the HF RFID technology.
Not every HF RFID tag can be a NFC tag, but all NFC tags are HF RFID tags.
There is a highly specific subset in the high-frequency range (13.56 MHz) where NFC operates.
Compared to the other categories of RFID, they have various implementation considerations and use cases.
Main Differences Between NFC and other RFID categories
Among the NFC tags’ main difference is that it has a read range that is smaller.
Thus, it often requires the tag and the reader to not be more than several centimeters away from each other.
Even if there are other types of RFID that allow whole pallets of tags to get read immediately, you need to have the NFC tags read one at each time.
However, since NFC tags have capabilities for two-way communication and bigger memory, they can be highly useful in communicating and storing larger groups of information, which is why this tool can be incredibly valuable in promotional campaigns.
NFC Tags and Their Applications
The use of NFC technology can be quite useful in contactless applications for payment like ApplePay™ as it provides one-to-one secure coupling.
Since almost every smartphone can function as an NFC reader, the NFC tags have been famous in promotional posters and labels.
This tool can be great in providing personalized engagement for the customer.
RFID Tags that are Semi-Passive, Active, and Passive
Since active RFID tags come with a battery that periodically transmits signals, they can be useful in applications that track location.
Since signal strength can get boosted by the battery in the active tags, they have the tendency to provide a read range that is longer, which can be a maximum of 100 meters.
Until they get the reader’s radio signal, passive tags stay dormant.
The signal of the reader has an energy that you can use to have the tag turned on and reflect the signal that carries the information back to the reader.
RFID tags that are battery-assisted or semi-passive have a battery, but they are not similar to the active RFID tags that transmit signals periodically.
Instead, they only use the battery to have the tag turned on whenever you receive a signal.
With this, all of the energy from the signal of the reader gets reflected back.
Since active tags have the tendency to be more costly, people often use them whenever they want to track assets of really high value, like the equipment that people use in healthcare, automobile, and construction industries.
When it comes to labels for the pallet and products, people most widely use NFC or near field communication.
Disadvantages of RFID
While yes, there are many benefits to RFID technology, RFID is not without its problems which include various technological and security issues.
Since it can be difficult for the RFID tag to distinguish the readers, almost anyone can read the information whenever it leaves the original chain of supply.
For this reason, the portability of RFID readers as well the great range of certain tags can allow scammers to gather information that they would not have access to otherwise.
Scammers are able to gather the information that can be potentially sensitive without the knowledge of that person.
For consumers, there is another concern when it comes to the security of RFID tags – since they can get linked to any individual credit card, there is a great potential for financial fraud or theft.
In terms of technology, it can be problematic to use RFID tags mostly because of the absence of real industry and global standards.
Their usability can get reduced because they can become easily disrupted or jammed as radio frequency is what they operate on.
It can result in decreased productivity and extended waiting times in both warehouse and retail settings.
There may also be signal problems that can happen with the RFID inventory systems.
It includes collision that happens whenever signals from a couple or more readers overlap and the surrounding area has interference due to magnetic fields, water, or metal.
Setting up the RFID system can also be labor-intensive and time-consuming, as well as costly.
Thus, companies would have to test out different tag systems and hardware if they want to know the best fit that could take months for arrangement.
Aside from the expenses involved in getting an RFID system like the RFID scanners and the tags, you may also have to spend more because of the additional need for labor and time.
You can often avoid these disadvantages whenever you use barcodes.
That is why a lot of businesses still consider them popular in controlling the inventory and collecting the data.
Conclusion
Since the active RFID constantly sends out a signal, it can be a great choice for anyone who is searching for live, up-to-the-minute tracking like real-time applications in vehicle tracking and tolling.
As a costly product, they can offer the long read range that people can prefer depending on where or how they may be applied.
Compared to the active RFID tags, the passive RFID tags are highly economical as each of them just costs approximately 20 cents.
They are commonly used for file management, applications for access control, race track, and supply chain management.
An RFID tag that is passive would not require being directly in the RFID reader’s line of sight.
However, compared to the active RFID tag, it has a read range that is much shorter.
Since they have a small size that makes them lightweight, they have the potential to last for a lifetime.
A highly rugged and bigger design are what active RFID TAGS features compared to the passive RFID tags.
Because of that, they are highly suited to become applied whenever durability is vital.
People can frequently use them in applications for cargo tracking, transponder systems for toll payment, as well as devices that can be used in tracking people.
RFID tags have many uses and hopefully you are more knowledgeable on how they work and htey can be implemented in the real world.
Know About the Best RFID Tags with IRDA

With IRDA, you can know the best information about Radio Frequencies, Infrared Technologies, WiFi, and 3G.
We have a team of Electronics Technicians and Tech Engineers that believes people should be able to safely use their electronic devices and appliances.
Since that is the case, IRDA is committed to giving people highly informative and well-researched information on Electronics, WiFi, Electro-Magnetic Fields, and more!